| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
If your Windows version does not have ssh in Command Prompt or PowerShell:
More advanced options for those who want a full Linux environment on their Windows system:
|
From now on, when we refer to "Terminal", it is either the Mac/Linux Terminal program, Windows Command Prompt or PowerShell, or the PuTTY program.
...
- Answer yes to the SSH security question prompt
- this will only be asked the 1st time you access ls6
- Enter the password associated with your TACC account
- for security reasons, your password characters will not be echoed to the screen
- Get your 2-factor authentication code from your phone's TACC Token app, and type it in
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
If you're using PuTTY as your Terminal from Windows:
|
...
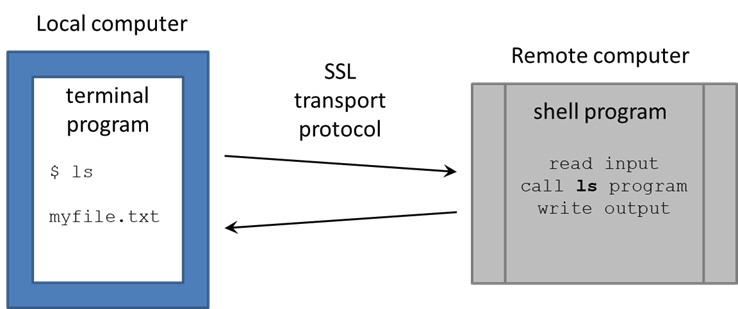
The Terminal is pretty "dumb" – just sending what you type over its secure sockets layer (SSL) connection to TACC, then displaying the text sent back by the shell. The real work is being done on the remote computer, by executable programs called by the bash shell (also called commands, since you call them on the command line).
About the command line
...
Now execute the lines below to set up a login script, called ~/.bashrc. [ Note the tilde ( ~ ) is shorthand for "my Home directory". See See Linux fundamentals: pathname Pathname syntax ]
When you login via an interactive shell, a well-known script is executed to establish your favorite environment settings. The well-known filename is ~/.bashrc (or ~/.profile on some systems), which is specific to the bash shell.
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# show a long listing of all files in the current directory, including "dot files" that start with a period ls -la |
(Read more about File attributes)
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
What's going on with chmod? The chmod 600 ~/.bashrc command marks the file as readable and writable only by you. |
...
| Tip |
|---|
$WORK and $SCRATCH are TACC environment variables that refer to your Work and Scratch file system areas – more on these file system areas soon. (Read more about Environment variables) |
| Expand | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
The ln -s command creates a symbolic link, a shortcut to the linked file or directory.
Want to know where a link points to? Use ls with the -l (long listing) option.
|
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
ls $CORENGS |
(Read more about Environment variables)
Shell completion with Tab
...
Here's how the common login script adds the ~/local/bin directory you created above, to the location list, along with a special dot character ( . ) that means "here", or "whatever the current directory is". In the statement below, colon ( : ) separates directories in the list. (Read more about pathname Pathname syntax)
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
export PATH=.:$HOME/local/bin:$PATH |
...